- Abstract
Object: The subject of the study is the study of ways to optimize regulatory mechanisms and support from the state, if the investment situation of the regions of Kazakhstan has determined as a purpose the study to show the most effective ways associated with their increase, forming the object of study
Methods: statistical analysis, integral potential, methods of integrated risks
Findings: The investment climate in the country is the main factor determining the ability of the country to attract foreign investment, as well as the development of small and medium enterprises. From this point of view, the problem of increasing the investment opportunities of the regions and acquiring on their basis the opportunities for the development of small and medium-sized enterprises is one of the most urgent. Therefore, in the article, a comparative analysis of the investment priorities of the regions reflects the relevance of the full implementation of strategically important state programs.
Conclusions: The modern mechanisms of state support and regulation of investment attraction processes, indicating the causes of imbalances in the regions of the Republic of Kazakhstan are reflected in this article. Given the diverse industrial and industrial focus of the regions, the need for ongoing support for economic diversification has been taken into account.
Introduction
Attracting investment in the economy of Kazakhstan is an objectively necessary process. Obviously, this process will contribute to the structural modernization of the economy, the creation of new high-tech industries, the revitalization of fixed assets, the technical re-equipment of many enterprises, the training of specialists, the introduction of advanced management achievements, marketing and know-how, and the saturation of the domestic market with high-quality domestic goods and at the same time to increase exports to foreign countries.
From this point of view, the relevance of the “investment climate” of the country to attract foreign investment and increase it from the point of view of state regulation is very high.
Literature Review
By the end of the 20th century, all conclusions regarding the concept of “investment” began to be explained by a general and generalized approach to various investments aimed at increasing income. It is known that the historical evolution of the scientific nature of the investment climate manifested itself in the works of several foreign and national authors. In particular, with the names of such authors like P. Masset, J. Keynes, P. Heine, L.J. Gitman, M.D. Jonck, V.D. Nikifirova, national scientists M.T. Ospanov, T.I. Mukhambetov, N. K. Nurlanova (Saiymova et al., 2018).
A number of modern foreign authors in their works proceeded from the fact that the optimal conditions for the development of the country's economy directly depend on the investment climate (Orynbassarova, 2017, 224)
According to the national scientist N.K. Nurlanova “... the Kazakhstani regions are characterized not only by the state of natural-climatic and raw materials, but also by the diversity of their economic potential, the quality of human capital and the investment climate” (Kireeva et al., 2018).
Methods
Attracting foreign investment has a significant impact on the growth of the country's economy as a whole, but not all of them have the same effect. The variety of investments depends on the variety of motives created
to attract them. The only way to classify investor motivation was proposed by British economist John Dunning (Tchouassi, 2014).
It is classified on:
- – investments in natural resources: is determined by the access of investors to the use of natural resources;
- – investments aimed at the market: is determined by the ability of investors to work in the domestic or regional markets;
- – investments aimed at improving efficiency: is determined by the orientation of investors to rich a profit from factors of high competitiveness in the international market (for example, one of the types of production, IT services, etc.).
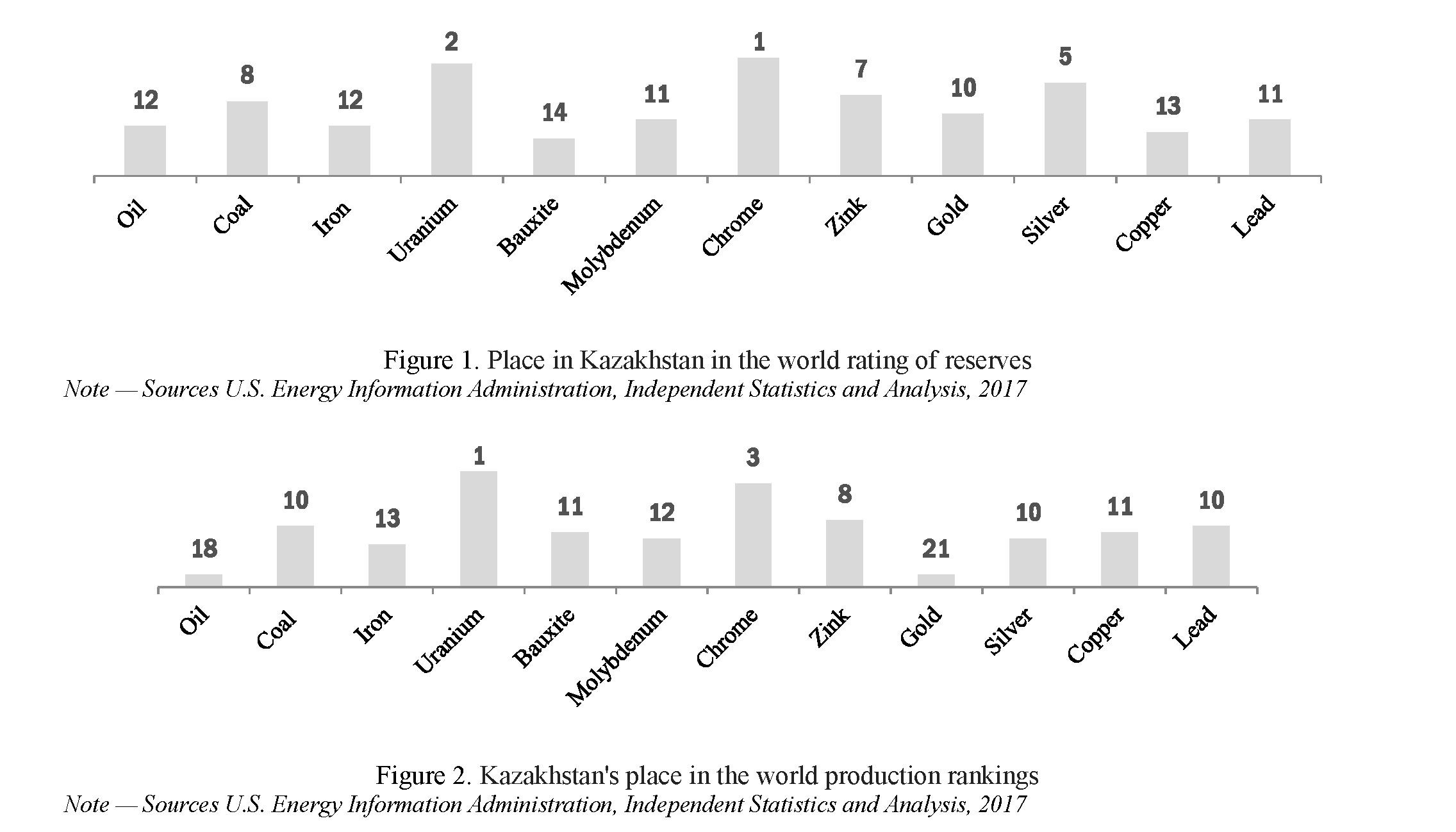
The investment attractiveness of the economy of Kazakhstan is ensured by access to natural resources, sustainable development, the geostrategic location of Kazakhstan and the availability of an appropriate legislative framework (Fig. 1, 2).
Investments aimed at improving efficiency are the most effective for diversification, however, this way of attracting investment is relatively difficult.
Several approaches are known for assessing the investment attractiveness of regions. In particular, we can call the method of “total (integral) potential” (consists of 9 elements, such as consumer; production; financial; infrastructure; labor; natural-resource; institutional; innovative; tourism potential) and “integral risks” methods (consists of 6 elements, such as social; economic; financial; criminal; managerial; environmental risks). Integral assessment indicators give a rating method of the investment climate. It is based on the following formula (1):
The value "K" contains an interval from 0 to 10. The higher is it, the more the region has a favorable situation. Disadvantages: insufficiency of evaluated characteristics and inaccuracy in the assessment of component indicators.

Results
Improving these areas, which are recognized theoretically and practically important for attracting investment in the economy of Kazakhstan, is carried out as part of the “National Investment Strategy”. This strategy is aimed at increasing and diversifying investments, forms the country's investment forecasts and contributes to the achievement of the goals of modernization and development of the economy of Kazakhstan.
The following programs have been adopted and are being implemented in our country within the framework of the state strategy to support investment: “Business Roadmap 2020”, “Agribusiness 2020”, “Exporter 2020”, “Productivity 2020”, state support for industrial and innovative development.
The main goal of the strategy is characterized by ensuring the growth and modernization of the economy of Kazakhstan by increasing the flow of foreign direct investment (FDI) and diversifying its structure (Table 1).
Analysis of the investment activity of the country's economy is achieved on the basis of the following tasks:
- The definition of “growth points” of investment activity, which will depend on the future growth of the economy.
- Preparation of data for predicting the state of investment activity.
Determining the directions of investment policy and investment in specific projects and programs (Abe- nov et al., 2019).
Table 1. Foreign direct investment breakdown, bln $.
|
Foreign direct investment |
Key figures, year of 2016 (bln. $) |
Target indicators, year of 2022 (bln, $) |
Growth, % |
|
Key figures of FDI |
20.6 |
26 |
26 |
|
Focused on resources |
12 |
13.8 |
15 |
|
Focused on a market |
4.8 |
6.5 |
34 |
|
Focused on efficiency improvement |
3.8 |
5.7 |
50 |
|
Note — Composed by the authors on the basis of the materials of the book (Putevoditel investora, 2017) |
|||
There is every reason to fulfill these tasks and no doubt evaluate the implementation of plans and forecasts within the framework of the “National Investment Strategy”, including the potential opportunities in the country given above. Along with the resource attractiveness of the country, one of the factors that directly affect another investment climate is the country's tax system. The most common benefits at this location can be estimated based on the following comparative indicators (Table 2).
Table 2. Comparative indicators of basic taxes
|
Kazakhstan |
Russia |
China |
|
|
Corporate income tax (CIT) |
20 % |
20 % |
25 % |
|
Value added tax (VAT) |
12 % |
18 % |
17 % |
|
Land tax |
0.03-0.16 USA $ per 1 m2 |
0,3 %, 1,5 % |
- |
|
Real-estate tax |
1,5 % |
2,2 % |
1.2 % estimate value, 12 % leased property |
|
Note — composed by the authors |
|||
Under the general investment activity is understood the system of economic relations of individuals or legal entities associated with investments in fixed assets, construction and installation works and machinery, equipment, tools, as well as in housing construction (Saparova, 2015).
Features of modern directions of development of the investment process in Kazakhstan, their social content can be characterized as follows:
- Kazakhstan is one of the main states that accept foreign capital in the post-Soviet space.
- Despite the outstripping inflow of investments, the inflow of foreign capital into Kazakhstan is still insufficient.
Of course, foreign investment is currently contributing to the active growth of the economy in any country. They play a large role in the process of demonopolization of the economy of Kazakhstan, contribute to free competition, development of production, the formation of market mechanisms for regulation and stimulation and allowed to get out of deep inflation thanks to the measures taken.
- One of the following cases, on which it is worth focusing attention is the fact that foreign residents contribute has mainly developed on the process of direct investment in Kazakhstan. For example, the US share is above 36 %, the UK is 17 %. Italy — 12.8 %. Next are South Korea, China, Canada and other countries. And the share of the nearest neighboring state is only 6 % of direct investment.
- The main form of attracting direct investment in the republic was the joint ventures of the oil and gas industry and companies separated from the existing enterprises. In this regard, it should be noted that the share of oil and gas companies in taxes and other payments covers a significant part of the state budget. In addition, revenues in the form of over-planned income tax, royalties, bonus and other types from these companies make up the major part of the National Fund.
- The main feature of the development trends of the investment process is its focus on the extraction of raw materials.
- The existing positive features of the investment process include the recent decline in foreign investment and the growth of domestic internal investment.
- The next emphasis is on increasing the role of the state in financing investment activities. As world experience shows, role of the state in reducing, in whatever area from developed countries, its services for regulating investments in the most important sectors of the economy should be especially systemic.
It is advisable to be familiarized with the sources of financing after considering indicators of investment in fixed assets. So, investments in fixed assets are financed from budgetary funds, own funds, foreign investments, borrowed funds.
In terms of economic content, investments form a part of the social product aimed at creation and reconstruction of fixed assets. In general, investments in fixed assets determine the material and technical development of the national economic complex of the state and are aimed at increasing the production capacities of industry, agriculture and other sectors of the economy, as well as to meet the social needs of the population.
If we talk about the investment potential in the regions of the Republic of Kazakhstan, then the investment potential of the republic can be represented in a natural way, combining into five main regional groups:
- - The Central-Eastern zone (Karaganda, East Kazakhstan, Pavlodar region) -concentrates more than 30 % of the investment potential of Kazakhstan. Of great interest to investors are coal mining, electricity, ferrous and non-ferrous metallurgy, heavy engineering;
- – South- Eastern zone (Almaty and Almaty regions) — the share of the investment potential of the Republic is about 25 %. The food industry, light industry, pharmaceutical industry and mechanical engineering are developed in this region;
- – The northern zone (Nur-Sultan, Akmola, Kostanay and North Kazakhstan regions) — makes up 18 % of the investment potential of Kazakhstan. In this region there is a transport-geographical position and a developed infrastructure of the economy. Bauxite and iron ore are produced here. Interest for investors is agriculture;
- – The western zone (Aktyubinsk, Atyrau, Mangistau and West Kazakhstan oblasts) consist 16 % of the republican potential. First of all, this is the zone of oil and gas resources and oil and gas production, which role in the economy of Kazakhstan is constantly growing;
- – The southern zone (Kyzylorda, Zhambyl and Turkestan regions) — 11 % of the total potential. It has developed agriculture, oil refining, food and chemical industries, gold and barite are being mined (Table 3).
Depending on the production orientation of economic sectors, as indicated in table 3, the degree of “investment attractiveness” can be differentiated. Along with these opportunities and potential, the necessary conditions for investing in the following areas have been optimized. In particular:
- – In the framework of the “National Investment Strategy”, “incentive measures” have been adopted and work in the country since 2014. In particular, incentives for priority investment projects (key priority criteria are compliance with the list recognized by priority activities (approved by the Government of the Republic of Kazakhstan) for newly established company (investment of at least $20 million) are as follows;
- – The legislative stability. In particular, the stability of tax legislation in relation to types of taxes, except VAT and excise taxes;
- – Simplification of the visa regime. Methods of introducing a visa-free regime in some countries, at certain intervals, benefits for hiring labor, the removal of special permits (temporary) in respect of foreign manpower etc.;
- – Tax exemption (temporarily in the amount of 0 % on corporate income tax, land tax and property tax));
- – Investment subsidies — cost recovery up to 30 %
- – Protecting investor rights. Ombudsman Offices: in order to protect the legitimate interests and rights of investors, the Ombudsman: 1) makes decisions on issues arising in the activities of investors, as well as in relations with government bodies; 2) helps to find out-of-court and pre-trial decisions on investors` issues.
Table 3. Main economic sectors by cityes and regions
|
Areas |
Major industries |
|
Nur-Sultan |
Field of activity; Construction and production of building materials; food industry; public services; financial sphere; social sphere |
|
Almaty |
Field of activity; construction; trade; operations with real estate; transport and communication; industry |
|
Akmola region |
Agricultural products; chemical and pharmaceuticals; production of building materials; engineering; mining of ores containing uranium and gold; non-ferrous metallurgy |
|
Aktobe region |
Ferrous metallurgy; engineering; oil producing; chemical and light industry; mining industry |
|
Almaty region |
Agricultural production; sphere of trade; food production, tourism |
|
Atyrau region |
Oil and gas; mining industry; transport and storage industry |
|
East-Kazakhstan region |
Non-ferrous metallurgy; metalworking; engineering; agricultural products |
|
Karaganda region |
Mining industry: mining of non-ferrous and ferrous metals, noble and rare metals, coal basin; chemical production; food industry; pharmacy |
|
Kostanay region |
Agriculture; mining and processing of iron ore; asbestos production |
|
Kyzylorda region |
Oil and gas production; mining; agriculture |
|
Mangistau region |
Oil and gas production; manufacture: chemical production, engineering |
|
North Kazakhstan region |
Agriculture; food industry; engineering; forestry and fisheries; manufacturing industry |
|
Pavlodar region |
Aluminum industry; coal mining; ferroalloys; electric power industry |
|
Turkestan region |
Agriculture; processing industry; uranium mining |
|
West-Kazakhstan region |
Gas production; industry; construction; transport and communication; agriculture |
|
Zhambyl region |
Agriculture; food and chemical industry; mining; manufacture |
|
Note — Systemized and composed by the authors |
|
The favorable climate characterizing these incentive measures is carried out on the basis of special economic zones created within the territory of Kazakhstan.
Kazakhstan in its investment policy is focused on creating favorable conditions for investors. An investor can invest in a profitable industry located in regions with a high risk of investing, or invest in inefficient projects in “quiet” areas for an investor. To find “investment optimization” will help the distribution of the regions of Kazakhstan in the groups presented in table 4.
The objectives will be achieved on the basis of strengthening the integration of the business sector of the economy and the state, accelerating the introduction of modern investment and financial mechanisms, attracting non-state and foreign capital in the field of science and technology (Golub, 2017, 139).
In general, the investment climate of the regions consists of two main elements — indicators of investment attractiveness and investment activity.
The investment activity of the regions is largely characterized by the volume of investments in fixed assets, and the investment attractiveness directly depends on the level of “favorable” conditions created for investors in this region and their assessment by investors.
As can be seen from table 4, all regions of Kazakhstan are divided into three main groups. Each of these groups is distinguished by the characteristics of the investment climate. Optimal for the conditions of Kazakhstan is the Group, which includes Pavlodar, Atyrau and Almaty regions. They are characterized by the presence of a sufficiently high potential and medium risk (Sabirova, 2017).
Table 4. The division of the regions of the Republic of Kazakhstan by groups depending on the level of investment attractiveness
|
Characteristics of the investment climate |
Regions |
|
|
1 group |
High potential and high risk |
Karaganda and East Kazakhstan region |
|
2 group |
Limited investment potential combined with possible minimal risk |
Nur-Sultan, Aktobe, Zhambyl, West-Kazakhstan, Ky- zylorda, Mangistau, North-Kazakhstan and Turkestan regions |
|
3 group |
High investment potential combined with medium risk |
Pavlodar, Atyrau and Alamty regions |
|
Note — composed by the authors |
||
The volume indicators of investments in fixed assets by regions of Kazakhstan in 2018 can be seen in figure 3 below.
Based on the rating of the investment climate, the regions of Kazakhstan can be placed according to the ordinal method, as shown in table 5.


regulators. As a result, most regions of Kazakhstan need to attract large-scale investments and an effective mechanism for managing investment processes, taking into account local business requirements and the existing potential in the region (Niyazbekova, 2016).
An imbalance in the development of the region is not a unique phenomenon that is unique only to Kazakhstan. Solving this issue requires an integrated approach combining industry-specific approaches, including strategic long-term development plans, developed considering the regions and their competitive advantages, measures related to supporting entrepreneurship in order to ensure employment and increase the welfare of the population.
Discussions
The government of Kazakhstan is working on eliminating the imbalance in the development of the region. For this purpose, an action plan has been developed aimed at the effective disclosure of the economic potential of the regions, as well as improving social and physical infrastructure. The main activities under this plan include actions by the government and local authorities aimed at identifying economic growth centers around the region. In order to provide citizens with state services of a uniform quality level, regardless of their place of residence, intergovernmental relations are being improved. In connection with the increase in the investment climate in the regions of the country, it is possible to propose a common network of ongoing events and activities recognized as necessary for holding, with a breakdown, grouping:
1. Search and sponsorship measures for foreign investors in the regions: priority investor countries; establishing relationships with investors directly or through partners in priority investor countries; information and consulting support; organization of meetings at the local level; support (support) of investors in the regions.
2. Promotion of the investment image: National Investment Interactive Resource www.invest.gov.kz; database of foreign investors and investment projects www.baseinvest.kz; road show; brochures on investment opportunities in Kazakhstan; video clips; billboards; press conferences.
Post-investment: a center for foreign investors; ombudsman
In order for our investment climate to be more favorable, and Kazakhstan to become a leader in the volume and quality of attracted foreign investment, political will and special actions are necessary.
In the field of attracting foreign direct investment (FDI) in the international market, it is necessary to improve the quality indicators in the country in order to be successful competitive and increase the share of value added. The following could be included to this indicators:
– development level of transport infrastructure and logistics;
– transparency and predictability of the regulatory environment;
– the availability of research and development work (R&D);
– development of human resources in accordance with the needs of the economy and innovation.
Kazakhstan shows high rates of attracting FDI, especially in the extractive industries. In implementing large-scale plans to diversify the economy and develop priority sectors, the country needs foreign investors with specialized knowledge and high technology, such as strategic partners — Japan, China. In order to attract and retain such investors, it is necessary to develop a regulatory environment and law enforcement practice, infrastructure, develop human resources, actively cover investment opportunities in various sectors and further improve investment incentive measures. To increase its competitiveness and investment attractiveness, the country needs to find its place in the international economy and work out the principles of an integrated approach to attracting investors and continue to remove barriers to FDI. FDI policies should be based both on attracting new investors and on stimulating investors operating in the country.
In Kazakhstan, within the framework of economic diversification, priority sectors have been identified. The list of priority sectors can be placed as follows: metallurgy (ferrous and non-ferrous) — chemical industry (agrochemistry-production of chemicals for industry) — petrochemical industry (oil refining-petrochemicals) — mechanical engineering (automobile production — electrical equipment — agricultural machinery production — w / w d technicians — mining equipment — oil extraction and processing equipment) — production of building materials — food industry.
The work related to the development of industries can be intensified by attracting and stimulating strategic foreign investors. They can play an important role in supporting accelerated economic development through the transfer of new technologies and knowledge, as well as in the creation of a value chain involving local enterprises.
By stimulating investments in the unproductive sector of the economy, Kazakhstan seeks to further develop a diversified economy and seeks to increase the pace of economic development and employment growth in the country (Beisengaliev, Turekulova, 2015, 24).
All agroindustrial economy — all sectors in agriculture from primary production processes to finished products and bringing them to the consumer need reconstruction and modernization.
Conclusions
In the direction of attracting investment in the economy of Kazakhstan, including on the basis of economic development and the capabilities of the regions, the government provides for activities in three main areas. Such as:
- – Optimization of the investment climate. Implementation of fundamental reforms in order to increase the investment competitiveness of Kazakhstan and its regions;
- – Promotion of investments (provision of state support for the correct implementation, starting with advertising, etc.) and positioning in international markets;
- – Privatization and public-private partnerships (measures to attract strategic investments).
The most frequently encountered difficulties of investors should be carried out in the following areas of state regulation: tax and customs legislation; visa, migration, labor legislation; legislation in the field of construction and licensing; legislation governing land relations.
At the same time, we believe that the government's regulatory measures to increase the investment climate in the regions of our country will concern the following measures:
1.It is important to take measures to create a favorable investment climate in order to attract investment in the non-resource sectors of the economy, namely: the introduction of OECD standards; expanding the range of services for the "single window"; providing guarantees from legislation for investors; diversifying sources of investment.
2. Development of the legislative and institutional framework for public-private partnerships: revision of some of the “weaknesses” of the adopted law “On PPPs”: to ensure long-term urgency and stability of relations with investors, to expand the financial mechanisms of PPPs and transparency of private sector interaction with the state; “Single window” on PPP; further identification of PPP development projects and priority sectors.
- Conducting the second stage of privatization.
This network of government regulation measures recognized in our country should contribute to the solution of the following issues:
- • informing about the benefits and priorities;
- • reduction of dependence in the oil and gas sector;
- • the development of social infrastructure and the health system (which, in turn, eliminates the unevenness of the regions);
- • improving the transparency of the regulatory environment (to improve the business climate);
- • measures to encourage innovation;
- • the development of new technologies, training (in order to increase innovation).
Thus, investments are considered as a universal tool for solving all issues related to overcoming the investment crisis, and should play the role of a sufficiently strong catalyst in the investment process. Kazakhstan should become a new investment hub in non-resorce sectors.
References
- Abenov, Y.M., Kirdasinova, K.A., Tulaganov, A.B., Zhumataeva, B.A., Mutalyieva, L.M. & Issayeva, B.K. (2019). Entrepreneurship education: Teaching and learning modern mechanisms of entrepreneurship development based on public-private partnership. Journal of Entrepreneurship Education, 22(5), 134–141.
- Imangozhina, Z., Satenova, D., Niyazbekova, Zh., Zuyeva, A. & Issayeva, B. (2019). Development of trade and economic cooperation in the oil and gas sectors between Kazakhstan and Russia. Proceedings of the 1st International Scientific Practical Conference “The Individual and Society in the Modern Geopolitical Environment” (ISMGE), DOI: https://doi.org/10.2991/ismge-19.2019.54
- Kashuk, L.I., Bekniyazova, D.S. & Soltangazinov, A.R. (2018). The analysis of state and efficiency of entrepreneurial activity's development of the Pavlodar region. Bulletin of the Karaganda University. Economy series, 4(92), 193– 199.
- Kireeva A.A. & Nurlanova N.K. (2018). Intuitional and Economic Mechanisms for technological Modernization of Regions in Kazakhstan. Problems of territory's development, 4 (96), 34–41.
- Niyazbekova, Sh., Grekov, I. & Blokhina, T. (2016). The influence of macroeconomic factors to the dynamics of stock exchange in the Republic of Kazakhstan. Economy of region, 4 (12), 1263-1273, DOI: 10.17059/2016-4-26 Orynbassarova, Y., Legostayeva, A., Omarova, A., Ospanov, G. & Grelo, M.F. (2017). Development of financial support of innovative activity in the Republic of Kazakhstan. Bulletin of the Karaganda University. Economy series, 4(88), 224-230.
- Sabirova, R.K., Karamuldina, A.A. & Tlepova, G.B. (2017). Atyrau region current energy status. Bulletin of the Karaganda University. Economy series, 4(88), 46-52.
- Saiymova, M., Dzhusibalieva, A., Baimukasheva, Zh. & Turganbaev, M. (2017). Features of social and economic development of the small city of Kandyagash. International Journal of Economic Perspectives, 4 (11), 125-130.
- Saiymova, M., Smagulova, Sh., Yesbergen, R., Demeuova, G., Bolatova, B., Taskarina, B. & Ibrasheva, A. (2018). The Knowledge-Based Economy and Innovation Policy in Kazakhstan: Looking at Key Practical Problems. Academy of Strategic Management Journal, 6(17), 1-11.
- Saiymova, M., Turganbaev, M., Taskarina, B. & Shakibaev, M. (2014). Regional development: Input-output analysis, issues of improvement. Live Science Journal, 11(10s), 219-224.
- Semenyuk, O., Abdrashitova, T., Beloussova, E., Nechay, N., Listkov, V., Kurbatova, V. & Niyazbekova, S. (2018). The influence of ecology and economic factors on eco-architecture and the design of energy efficient buildings. World Transactions on Engineering and Technology Education, 2 (16), 186-192.
- Tchouassi, G. (2014). Private Capital and Investment Climate for Economic Growth: Empirical Lessons based on ARDL bound test technique. European Journal of Sustainable Development, 3, 17-32.
- Zhansagimova, A., Azatbek, T. & Niyazbekova, S. (2013). Model of organizational structure for tourist cluster in Kazakhstan. Актуальні проблеми економіки, 11 (149), 332-337.
- Beisengaliev, B.T., & Turekulova, D.M. (2015). Investitsionnaia privlekatelnost regionov RK [Investment attractiveness of the regions of the Republic of Kazakhstan]. Vestnik KazNAU — Bulletin of KazNAU, 4, 19-25 [in Russian].
- Golub, A.A. & Utegenova, A.M. (2017). Rol gosudarstva v sozdanii blagoprijatnogo investicionnogo klimata i analiz tekushhego sostojanija i perspektiv razvitija faktorov investicionnogo klimata [The role of the state in creating a favorable investment climate and analysis of the current state and development prospects of investment climate factors]. Vestnik Karagandinskogo universiteta. Economy series, 2(86), 139–146 [in Russian].
- Saparova, B.S. (2015). Finansovyi menedzhment [Financial Management]. Almaty: Ekonomika [in Russian].