The task to examine the major issues of special proceeding institute as type of civil proceeding is set in the present article. Modern civil turnover includes the need to establish the existence of legal facts, determining the legal regime of the different private law relations and the establishment of the legal status of their participants in order to implement the rights of these subjects in the sphere of private law. These issues are resolved by the courts of general jurisdiction in a particular order. Civil legislation provides for protection of the legitimate interests of the participants of civil relations, which has not yet been broken, and not contested, but which also needs to be protected from the government because of the uncertainty of specific legal facts, the legal status of citizens, and so on. The special proceeding is existing to protect such interests. The special proceeding is the third type of civil proceeding, which protects the personal rights and interests in cases where such rights and interests are violated, in the event of the need to establish rights which are the basis for the implementation of these rights. In the course of special proceeding eliminate of legal uncertainties and inaccuracies in respect of the circumstances, actions or events, carrying out of the control for the legality of the activities of notaries and RACS, thus preventing legal conflicts may be.
The structure of several forms of civil proceedings - contentious (claim), and the special procedure of civil process, which was caused by the need to create special procedural rules in civil procedural law for a very long time was fixing.
Construction of several civil justice forms the majority of modern researchers associated with the tradition of Roman law, which allocated the disputed claim proceeding and indisputable (voluntary), and that in their opinion, was reproduced current civil procedural legislation of modern states.
As the legislative practice evidenced, such civil process construction acquired axiomatic nature and there is no doubt. However, statements and examples indicating another approach to constructing structures of civil process were at various times [1; 225].
Thus, when Charter of civil court proceedings 1864 was developing, as the proceeding of criticism on Code of laws 1857 found, that one of the significant shortcomings of the legislation existing at that time is to conduct of various legal proceedings. As you know, the Code of laws provided for a common order of judicial procedure, and four main features and sixteen special ones. According to the department of laws and civil affairs of the State Council such legislative decision caused the slowness of legal proceedings, the development of formalism.
Austrian Charter of Civil Procedure, 1895, also included the differentiation of civil procedure. Section II of this statute, called «Proceeding in the first instance courts», containing chapter V «Specific proceed- ings», which included the features of consideration of separate categories of cases: the proceeding on bill claims, proceeding on claims arising from the contract of property rental, proceeding in the arbitration court, proceeding on the claims for damages caused by ranks of the judiciary. In addition, in particular the proceeding included the writ proceedings [2; 155].
P.P. Zavorotko, G.J. Stephan believe that «the Soviet civil procedural law has also been characterized by the idea of fixing the various forms of civil proceedings» [3; 55].
The first Soviet regulations about civil proceedings distinguished two types of civil proceedings: claim and protective, which is sometimes called undisputed or ex parte.
Acting Civil Procedural Codes of the RSFSR do not provide a definition of special proceeding, although secured list of special proceeding cases. Special proceeding designed as indisputable. The attempt to determine the nature of a special proceeding was made in the time instruction of People's Commissariat of Justice of the Ukraine from January 4, 1924 (circular number 4). The special proceeding in this document was opposed to the claim one by two characteristics: a) the establishment of the right in the claim proceeding and the finding of fact in an uncontested one; b) the possibility of objections, the call of parties in claim proceedings and proceedings without the defendant in a special proceeding. There are no other sources, which in one or another way fixed the legal reasons [4].
Despite the isolation of special proceeding in the civil procedure, as a relatively independent, common
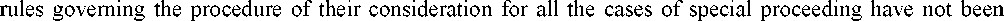
formulated in the Code of Civil Procedure of the USSR and a list of special proceeding cases and their corresponding rules of consideration was assigned. In accordance with the CPC of the RSFSR of 1995 and 1997 the cases of special proceeding these cases were:
- about property remaining after the dead;
- about the arbitration records and judgments;
- about the deposit;
- about issue orders for the acts;
d) about divorces, claims about the content and the establishment of children's names;
- about establishment of circumstances from the existence of which depends on the occurrence of public rights of citizens;
g) about exemption from military service on religious grounds;
h) about the complaints to the actions of notaries.
Later the Code of Civil Procedure of the RSFSR in the version of 1995 also provided for special proceeding. According to it, the cases of special proceeding concluded the case: about issue of injunctions; for permission to appeal indisputably penalties on current accounts and deposits with credit institutions; on establishing the circumstances that determine the appearance of the public rights of citizens; the renewal of rights to lost bearer securities; exemption from military service on religious grounds; complaints on the actions of notaries. In addition, according to the Code of Civil Procedure special proceeding cases concluded cases of divorce [5; 567].
As we can see, civil procedural legislation, enshrined the presence of protective (special proceeding), did not determine the criteria of these plants, their difference of action proceedings in a civil proceeding. The legislator only gave the list of cases referred to the special proceeding.
It was noted in the literature, that consolidation in the legislation of the two forms of civil proceedings has certain reasons, which are reduced to the fact that the nature of the special proceeding is determined by the absence of a dispute over a civil right in this proceeding. In contrast to the claim of cases the special proceeding cases resolved in a more simplified order, it does not apply some institutions of claim proceedings (settlement agreement, the rejection of a claim, third parties and others.).
The special proceeding is characterized as ex parte, unilateral proceeding with absentee disputing parties with opposing legal interests.
The essence of the special proceeding can be understood and disclosed only as a result of the analysis of the substantive legal and procedural nature of the cases referred to the special proceeding. And the nature of the proceeding purposes and ways in which the justice is carried out in special proceeding. Exactly these circumstances finally that ultimately causes the features of procedural order of consideration of special proceeding cases [6; 341].
Thus, the subject of judicial protection in the special proceeding cases is a legitimate interest of the applicant, mediated by the subjective right. The legitimate interest of social needs is understood in the jurisprudence, as social necessities taken under its protection by law by not granting them the carrier of subjective substantive rights, and providing to them (or others) the right to resort to judicial or other legal forms of protection [7; 270].
In this case, the protection of a legitimate interest in a special proceeding is needed for the applicant not exactly the most protection, or for the carrying out and acquisition of a subjective right in the future. Thus, the citizen must establish in court order the fact of its dependent on the deceased in order to ensure that this judgment on his application would the basis for the recognition of his legal heirs.
The special proceeding - is an independent type of civil proceedings in a specially within the jurisdiction of the court categories of civil cases, characterized by the absence of a dispute about the right and the use of special tools and methods of protection, in which the Court, by establishing of legal facts (actions, events, conditions) shall protect the interests protected by law citizens and organizations.
Legal regulation is possible only on the basis of not questionable legal facts. Implementation of the subjective right to a pension may be the case if you have installed the age of the person concerned, his seniority, disability, etc. For inheritance you need to know the facts of kinship certain extent, dependent, etc.
The special proceeding order established legal and evidentiary facts, and sometimes the conclusion of the legal status of a citizen or other legal issues resolve (on the basis of established facts, for example, a citizen recognized as missing or incompetent, or the issue of the transfer of property to state ownership addressed, and so on. For example, the fact of birth of a person is a legal fact, caused legal effect, but the fact of birth registration – evidentiary one.
There are two main procedures for establishing (ascertaining) of the unknown facts:
- administrative (including notary);
- court.
Obvious facts - birth, marriage registration, etc., ie, facts which are made directly in the face of the relevant body or confirmed by official documents may be certified in the administrative order. For example, the notary certifies the following facts:
- finding of citizen as alive;
- being of citizen in a certain place;
- identity of the citizen with the person depicted in the photo which is presented by this citizen;
- the presentation time to notary documents.
The facts are not clear, ie, either not subject to official registration or non-confirmed by official documents due to their loss, shall be certified by the courts, as they require examination of evidence supporting the relevant fact. If in the claim proceedings establishing of the relevant legal fact is necessary for the protection of subjective right, in special proceeding the applicant's interest is limited to a statement of fact. The question of fact arising from the subjective right decides later, outside the special proceeding [8; 144].
Due to the fact that the division on the life circumstances of legal significance and legally indifferent highly conditional and legally relevant facts is installed in the cases of special proceeding shall be determined specifically for each case. For determining of the legally relevant of fact it should be clarified the purpose of this fact, that the consequences of which the applicant would like to advance. Therefore, the fact is recognized as legal, if it has law-value to achieve the pursued goal by the applicant.
In addition, special proceeding can be set relatively large circle of evidentiary facts that is such, from the existence of which we can conclude on the presence (or absence) of the desired (legal) facts. So, the fact of birth of a person is a legal fact, attracted legal effect, and the fact of this birth registration - evidentiary fact. Therefore, the essence of special proceeding is to protect the legal interests through the establishment of legal or evidentiary facts [9; 199].
The court established the presence or absence of the following facts of different nature in special proceeding order:
- – actions - for example, the facts of registration of adoption (adrogation), marriage and divorce, inheritance acceptance, notary acts or refusal in their carrying out, and so on.;
- – events - such as the deaths at a certain time and under certain circumstances, birth, accident, etc.;
- – status – for example, a facts of person finding dependent, family relationship, the actual marital relationship, disability citizen, the citizen is missing, etc. [10; 229].
However, the concept and essence of the special proceedings, as well as the category of cases that are attributable to a special proceeding, in the science of civil procedural law are debatable. The theoretical problems of special proceeding are questions about the legal nature of the special proceedings, the subject of judicial activity and the list of special proceeding cases.
Exploring the question of the legal nature and scope of a special proceeding cilil procedural scientists have come to different conclusions [11; 223].
The main emphasis may be placed on the indisputable nature of the cases, which relate to a special proceeding. The main attention is drawn to the purpose of the procedural court activities directed at protecting the legitimate interests of citizens and organizations. The emphasis is on the subject of special proceedings, consisting in the establishment of the legal fact or condition, as well as overseeing the legality of the actions of the notary and racs.
Also, in a special proceeding legal and evidentiary facts established, and sometimes the conclusion of the legal status of a citizen or resolve other legal issues (on the basis of established facts, for example, a citizen recognized as missing or incompetent, or the issue of the transfer of property to state ownership addressed, and so on).
Chapter 31, Section 4 expressed the general terms of the special proceeding, the considered cases in this type of proceeding.
Cases of special proceeding are considered by the courts under the general rules of civil procedure with the exceptions and additions set out the civil procedural legislation [12]. General principles of civil procedure - legality, optionality, spontaneity, etc. are applied in special proceeding. Cases of special proceedings go through the same stages of civil procedure, which makes claim proceedings. The same rules of evidence, court record, judgments are all over on matters of special proceeding, etc.
The absence of the right dispute determines the specific features of the procedural forms of special proceeding. There are no parties (plaintiff and defendant). A person filing a case of special proceeding, called the applicant.
Related parties (citizens, organizations, financial bodies, social security bodies, etc.) are involved to participate in the cases of special proceeding. Third parties do not participate in the cases of special proceeding.
Failure to settle the dispute of the right in a special proceeding and the lack of action is due to non-use of typical claim institutions: the recognition and rejection of a claim, settlement agreement, maintenance of the claim, counterclaim, etc.
The list of cases considered in a special proceeding order defined by procedural law. These include cases.
Cases considered by the court in special proceeding order, includes cases:
1) about establishing the facts having legal significance;
2) on the applications for adoption (adrogation) of the child;
- about the recognition of the citizen as missing and declaring the citizen dead;
- about the limitation of legal capacity of citizen, deprivation of legal capacity, about restriction or deprivation of a minor under the age of fourteen to eighteen years old right to dispose of their income;
- about proclaiming of minor fully capable (emancipation);
- about the direction of minors into special educational organizations for children with deviant behavior or organizations with a special regime of detention;
- about the forced hospitalization of citizen into a psychiatric hospital;
- about the direction of the citizen to involuntary treatment of tuberculosis, alcoholism, drug addiction, drug abuse;
- about the restructuring of financial institutions and organizations within the banking conglomerate as a parent organization and non-financial institutions;
- about introducing, premature termination and extension time control grain-enterprise or organization of the cotton;
- about the rehabilitation and bankruptcy;
- about recognition of movable thing as ownerless and recognition of communal ownership of real property;
- about the establishment of civil registration irregularities;
- on complaints against notary acts or refusal from committing them;
- about the restoration of the rights of the lost bearer securities and order securities (procedure to declare lost documents void);
- on statements of recognition of organization carrying out extremist or terrorist activities on the territory of the Republic of Kazakhstan and (or) another state, extremist or terrorist, including the establishment of the changes it its name, as well as the recognition of information materials imported, published, produced and (or) distributed on the territory of the Republic of Kazakhstan, extremist or terrorist;
- on statements of recognizing online casino, product of foreign media, distributed on the territory of the Republic of Kazakhstan, containing information contradicting the laws of the Republic of Kazakhstan, unlawful;
- on statements of expulsion of a foreigner or a stateless person from the Republic of Kazakhstan for violation of the Republic of Kazakhstan legislation.
Also, the law may provide for the consideration and other cases in a special proceeding [12].
This group of cases considered by judge singly. In respect of certain categories of cases of special proceeding law clearly defines range of stakeholders, according to which proceedings may be instituted.
The composition of the persons involved into special proceeding is different from that participating in the claim proceeding. As there is no dispute about the law in cases of special proceedings, then there are no parties (plaintiffs and defendants), and third parties. Only the applicants and interested parties participate.
The prosecutor in the examination and resolution of certain cases of special proceeding required to participate in the force of law.
Summarizing, we can conclude that the special proceeding is one of the types of civil proceedings. The name itself indicates the presence of specific features that characterize a special proceeding.
Special proceeding - is an independent type of civil proceedings on a specially within the jurisdiction of the court categories of civil cases, characterized by the absence of a dispute about the law and the use of special means and methods of protection, in which the Court, by establishing legal facts (actions, events, conditions) shall protect the interests of citizens and organizations protected by law. Legal regulation is possible only on the basis of not questionable legal facts.
Yu.S. Chervonyi notes that «Special proceeding - type of civil proceedings, in order of which civil cases, which is confirmed by the presence or absence legal facts that affect the occurrence, change or termination of personal or property rights of citizens, or confirmed by the presence or the absence of an undisputed right, and defines the legal status of the citizen are considered» [13; 278].
Special proceeding is a type of civil proceedings, different from the claim one by the absence of dispute about the law and, as a consequence, the absence of the contending parties with opposing legal interests. Special proceeding is characterized as ex parte otherwise, one-sided proceeding.
Civil cases are considered in a special proceeding, which is required by the courts confirm the presence or absence of legal facts or circumstances from which depends on the occurrence, change or termination of personal or property rights of citizens. For example, a citizen may apply to the court with statement on the establishment of ancestral relations, as the establishment of this fact is necessary to join the right of inheritance or get the pension for loss of breadwinner.
Such civil cases for which it is necessary to confirm the presence or absence of indisputable right (such as the finding of possession and use of real estate, the cases of the restoration of the rights of the lost securities to bearer or order securities, on restoration of forfeited proceeding) may be considered within the special proceedings. At the considering of these categories of civil cases the court should resolve not only questions of fact, but also of law. In these cases, the protection of right cannot be realized in the claim proceeding, since there is no dispute about the right and the person concerned is no requirement to anybody. The cases in which the court determines the legal status of a citizen: in some cases, the citizen is recognized as incapable or partially capable; in others - is declared dead or declared missing are considered in special proceeding.
Referenses
- Komarov, V.V. (Eds.). (2001). Hrazhdanskii protsess [The civil process]. Kharkov: Odissei [in Russian].
- Treushnikov, M.K. (Eds.). (1998). Hrazhdanskii protsess [The civil process]. (2d ed.). Moscow: Spark [in Russian].
- Zavorotko, P.P., & Shtefan G.J. (1969). Neiskovoe proizvodstvo v sovetskom hrazhdanskom protsesse [Ex parte proceeding in the Soviet civil process]. Kiev: Kiev Universitu [in Russian].
- Porogov, A. (1999). Istoriia razvitiia osoboho proizvodstva [History of the development of special proceeding]. Pravovedenie – Legal Technology, 12, 45–51 [in Russian].
- Komarov, V.V. (Eds.). (2001). Hrazhdanskii protsessualnyi kodeks: nauchno-prakticheskii kommentarii [Civil Procedural Code. Scientific-practical commentary]. Kharkov: Odissei [in Russian].
- Musina, V.A., Chechina, N.A., & Chechot, D.M. (Eds.). (2001). Hrazhdanskii protsess [The civil process]. Moscow: PBOYuL Hrizhenko [in Russian].
- Vikut, M.A. (Eds.). (2005). Hrazhdanskii protsess Rossii [Civil process of Russia]. Moscow: Yurist [in Russian].
- Kazancev, V.I., & Kazancev, S.Ya. (2003). Hrazhdanskii protsеss [The civil process]. Moscow: Academiia [in Russian].
- Vikut, M.A. (Eds.). (2014). Hrazhdanskii protsess Rossii [Civil process of Russia]. Moscow: Yurist [in Russian].
- Yarkov, V.V. (Eds.). (2006). Hrazhdanskii protsess [The civil process]. Moscow: Volters Kluver [in Russian].
- Baimoldina, Z.H. (2001). Hrazhdanskoe protsessualnoe pravo Respubliki Kazakhstan [Civil Procedural Law of the Republic of Kazakhstan]. Almaty: KazHYuA [in Russian].
- Kodeks Respubliki Kazakhstan ot 31 oktiabria 2015 hoda № 377-V «Hrazhdanskii protsessualnyi kodeks Respubliki Kazhakhstan [Civil Procedural Code of the Republic of Kazakhstan dated October 31, 2015 № 377-V]. online.zakon.kz. Retrieved from https://online.zakon.kz/Dosument/ dos_id = 34329053 [in Russian].
- Chervonyi, Yu.S. (Eds.). (2003). Hrazhdanskii protsess [The civil process]. Kharkov: Odissei [in Russian].