Sustainable development management includes three major components: environmental, social, economic. This paper is focused mainly on environmental part.The article includeseconometric modeling approach in the analysis of environmental governance in the Republic of Kazakhstan on the way to sustainable development. We estimate regions in the Republic of Kazakhstan according to their economic and environmental development. Based on the above-mentioned we proposed 4 clusters. According to the analysis of environmental situation we found out that there is a need to minimize ecological consequences, future externalities for new generations. Public authorities need to understand it in the process of implementation of long-term social and economic strategy in the Republic of Kazakhstan. The prediction of the transition to «sustainable» development made by our macroeconomic model is very favourable for the Republic of Kazakhstan from economic, environmental and social points of view. In our model, it was shown that «sustainable development» not only leads to the economic development of the country as a whole, but also provides a higher GRP growth rate, smoothes uneven regional progress, and guarantees «development» itself one of the key indicators of the country’s well-being.
System of indices and indicators, which includes various components, is used to assess the level of sustainable development both at the regional and national level, as well as its modelling. In view of the availability of a huge variety of "sustainable development" definitions in the interpretation of domestic and foreign scientists, involved in the management of sustainable development, by sustainable development we understand a model of governance that will ensure a decent standard of welfare and dynamic development of economic and social system with the environment. A.A. Shalmuev in relation to socio-economic system defines "sustainability" in the most general form as the ability of the system to return relatively quickly to its original state or reach a new and higher point on the path of its development [1].
One of the most complete systems on coverage of sustainable development indicators was developed by the United Nations Commission on Sustainable Development. The indicators are divided into main groups:
- indicators of social aspects of sustainable development,
- indicators of economic aspects of sustainable development,
- indicators of the environmental aspects of sustainable development (including the characteristics of the water, land, air, other natural resources and waste),
- indicators of institutional aspects of sustainable development (programming and policy planning, research and development, international legal instruments, information technology, strengthening the role of major population groups) [2].
In this work we have attempted to analyze the relationship between the level of environmental pollution and the volume of GDP in Kazakhstan (in the whole country). In the basis we used the Environmental Kuznets Curve [3, 4] proposed by D. Grossman and A. Krueger [5].
Simplified Environmental curve regression equation is as follows:
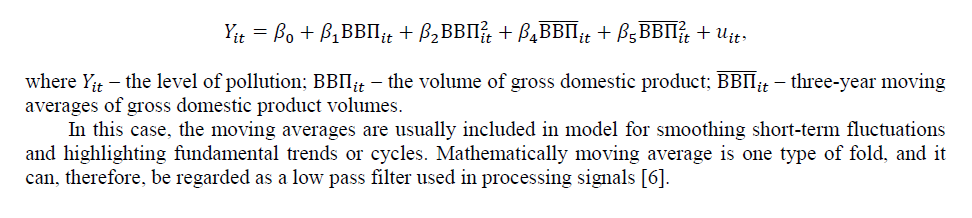


Carrying out similar calculations, we obtain a new matrix of distances.
We find again the minimum distance between objects d11,14 = 70, combine them into a cluster and on the principle of "distant-neighbour" define the distance between the clusters. Thus, re-construct a matrix of distances.
Calculations are continued for so long as one does not get the final cluster. The sequence of clusters join is represented in the form of the scheme:

On the basis of a schematic representation of the results of the cluster analysis, we can conclude that all regions of the Republic of Kazakhstan by ecological and economic development are divided into four clusters:
- Akmola region (1), Zhambyl region (6), Kostanay region (8), Kyzylorda region (9), North-Kazakhstan region (13);
- Aktobe region (2), Almaty region (3), West-Kazakhstan region (5), Mangystau region (10), SouthKazakhstan region (11), Pavlodar region (12), East-Kazakhstan region (14);
- Atyrau region (4), Karaganda region (7), Astana city (15);
- Almaty city (16).
The results of cluster analysis can be represented as a dendrogram, which is presented in Figure.


So, the first cluster is represented by the most prosperous regions in terms of ecology — Akmola, Zhambyl, Kostanay, Kyzylorda and North-Kazakhstan. For this cluster Kuznets curve does not work there is no maximum point, but we have minimum one, i.e. before it with the increase of GRP the emissions reduce, and after that point with increasing GRP the emissions will increase.
The second cluster is represented by less favourableregions from an environmental point of view: Aktobe, Almaty, West Kazakhstan, Mangystau, South Kazakhstan, Pavlodar, East Kazakhstan regions.
The third cluster is represented by Atyrau region, Karaganda region, Astana city; and the city of Almaty
stands out as an independent fourth cluster.
For all these regions ∩-shaped curve, i.e.there is a point of maximum GRP, after which emissions are reduced. That is, according to the environmental Kuznets curve, along with economic development the pollutants emissions into the environment reduce.
Why forthe first most prosperous cluster in the ecological sense in Kazakhstan Kuznets curve does not work?
This can be explained by the fact that the growth of economic activity has a negative impact on the quality of the environment; in contrast to changes in GNP income per capita, the impact on the environment of which is positive and linear, and this contradicts the results of Grossman and Krueger. Variable measuring the impact of trade is not significant in the regression equations, as it may have contradictory effects on the ecology. Researchers make the following conclusion: the level of contamination increases if the country has a surplus of capital (as in this case capital-intensive and environmentally dirty industries are developing), and decreases with growing labour-intensive industries.
In general, countries with low GNP income per capita generate polluting products, and the society is not so concerned about the condition of the environment that the government will realize conservation activity. With the growth, pollution reaches a critical point. Then the state under public pressure, on the one hand, begins to form a system of environmental management, and on the other with the help of macroeconomic tools to stimulate economic shift away from polluting industries to high-tech ones, in which modern technology and the human factor play an important role. As a result, environmental pollution begins to decrease.
So, the prediction of the transition to «sustainable» development made by our macroeconomic model is very favourable for the Republic of Kazakhstan from economic, environmental and social points of view. In our model, it was shown that «sustainable development» not only leads to the economic development of the country as a whole, but also provides a higher GRP growth rate, smoothes uneven regional progress, andguarantees «development» itself — one of the key indicators of the country’s well-being.
At the present stage of its development, the Republic of Kazakhstan has not yet reached the point of the maximum on the Environmental Kuznets Curve, which explains the environmental degradation and worsening of environmental situation.
A number of ministries, departments, committees, NGOs and other organizations responsible for addressing these issues in Kazakhstan practice the management of «sustainable development». The main government body, in our opinion, is the Ministry of Environment and Water Resources.
The transition to sustainable development and its management – is a very long process, as it requires the solution of unprecedented by scale social, economic and environmental objectives. As we move towards sustainable development the very notion of it will be changed and updated, the needs of people rationalize in accordance with environmental constraints, and means to meet these needs improve. Therefore, the implementation of the principles of sustainable development should be considered in stages. Moreover, only for relatively early stages appropriate software and forecast documents can be developed. For example, the Strategic Plan of the Ministry of Environment and Water Resources of the Republic of Kazakhstan for 2014 2018 years. This strategic document is a plan, which outlines the main objectives, indicators, events and measures to achieve the goals on the path to sustainable development in the Republic of Kazakhstan. But, unfortunately, many of the indicators of the Plan are not amenable to analysis and should be specified [8].
The transition of the Republic of Kazakhstan to sustainable development is predetermined by the need to address pressing environmental, economic and social problems. At the same time, programs of the environment improvement should be developed in the areas of ecologic crisis and begin their systematic execution; also outline comprehensive measures to normalize the situation in environmentally disadvantaged areas and prepare the organizational basis of these measures realization. Minimizing adverse environmental impacts, future externalities for the next generations is necessary. The problem of environmental constraints, compromise between current and future consumption should become the main in the elaboration of socioeconomic development strategy for the long term outlook for any country.
In the next step should be carried out major structural changes in the economy, technological innovation, and significant greening process of socio-economic development. At this stage, environmental wellbeing of the country is provided primarily through the rationalization of the use of the rich natural potential of Kazakhstan, the use of new technologies, the development of human capital and management.
References
- Antonova, M.A. (2013). Teoretiko-metodolohicheskie osnovy izucheniia ustoichivoho razvitiia rehionov [Theoretical and methodological foundations for the study of sustainable development of the regions]. Rehionalnaia ekonomika i upravlenie: elektronnyi nauchnyi zhurnal – Regional Economics and Management: an electronic scientific journal, 4(36), ISSN 1999-2645. Retrieved from http://region.mcnip.ru [in Russian].
- Indeksy i indikatory ustoichivoho razvitiia [Indices and indicators of sustainable development]. Retrieved from http://www.ustoichivo.ru/biblio/view/18.html [in Russian].
- Mikhail, Popov. Tolko by vyvezla. Ekolohicheskaia krivaia Kuznetsa slishkom khorosha, chtoby byt pravdoi? [Only be taken out. Is Environmental Kuznets Curve too good to be true?]. Smart Money 07.11.2006, 34 (34). November 24, 2014. vedomosti.ru Retrieved from http://www.vedomosti.ru/smartmoney/article/2006/11/07/1653 [in Russian].
- Kuznets, S. (1955). Economic growth and income inequality. American Economic Review, 5; Kuznets, S. (1963). Quantitative aspects of the economic growth of nations, VIII: the distribution of income by size. Economic Development and Cultural Change,
- Grossman, G.M., Krueger, А.В. (1991). Environmental Impacts of a North American Free Trade Agreement. National Bureau of Economic Research Working Paper. 3914.
- Skolziashchaia sredniaia [Wikipedia. Moving average]. ru.wikipedia. Retrieved from https://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki [in Russian].
- Komitet po statistike Ministerstva natsionalnoi ekonomiki Respubliki Kazakhstan [Committee on Statistics Ministry of National Economy of the Republic of Kazakhstan]. Retrieved from http://www.stat.gov.kz [in Russian].
- Stratehicheskii plan Ministerstva okhrany okruzhaiushchei sredy i vodnykh resursov Respubliki Kazakhstan na 2014–2018 hody [Strategic Plan of the Ministry of Environment and Water Resources of the Republic of Kazakhstan for 2014 2018]. April 25, 2014. Retrieved from http://eco.gov.kz [in Russian].