The article deals with the theoretical aspects of tax administration in the context of the provision of public services. It describes the main elements and the structure of the tax administration. The authors have determined that the tax administration is made up of government agency system that have the authority to collect revenue in a budget and a set of rules and regulations governing the tax procedure in the country. By studying the theoretical and methodological issues related to the nature of the tax administration and the tax authority functions in the system of public services, the authors' interpretation of the concept of «tax administration» has been given. The authors proposed the further development of the tax administration.
The potential of ongoing public administration reforms can be fully realized only with simultaneous improving of organization of public services provided by the tax authorities. Organization of the activities of the tax service of Kyrgyzstan and Kazakhstan in the provision of public services, that is, the tax administration has a significant impact on the socio-economic situation in these countries.
The current uncertainty of tax legislation in the field of tax administration in Kyrgyzstan and Kazakhstan gives rise to tax risks, both at the state level and at the level of taxpayers. And this has a negative effect on the development of tax potential. Unfortunately, modern science has not developed enough research of new approaches to the assessment of the largest taxpayers' tax potential and its instruments are not developed enough, too. A study of the theoretical and practical aspects of tax administration is directly related to the need for reform and improvement of the institute of tax law in order to ensure proper legal regulation of activity of the executive and the judiciary, in practice, creating a balance between public and private interests.
Tax administration is one of the main elements of the mechanism of management of public services. However, nowadays, the term «tax administration» is used haphazardly, there is no common understanding of its content. In the economic literature, a scientific discussion about the nature of the tax administration of its constituent elements, forms and methods of organization, role in the development of the tax systemis being conducted:
- tax administration is a complex of measures aimed at the full and timely payment of all taxes to the maximum extent at minimum cost;
- tax administration is a dynamically developing tax relationship management system that coordinates the activities of tax authorities in a market economy;
- tax administration is regulated by the norms of law activities of state bodies authorized in the tax area, aimed at the implementation of effective tax policy;
- tax administration is the organizational and management system implementation of tax relations, including a set of forms and methods, the use of which is intended to provide tax revenues to the budget system of the country [1].
In the presence of a wide variety of views we can distinguish two approaches to the interpretation of the content of this term. Tax administration in the broadest sense is understood as the tax relationship management system (tax system). Tax administration in the narrow sense is reduced to the tax control carried out by the tax authorities.
Tax administration as a special scientific and practical process is sufficiently capacious in content, organization and conditions of the target settings. This includes development of the legal framework of taxation on the basis of historical experience, modern achievements of economic science and practice, and providing conditions for the functioning of a particular tax mechanism elements (planning, control, monitoring), and the establishment of accounting and analytical, accounting rules, documents, and more. It is a leader in public service management system.
State tax administration as the quality of fiscal tax authority activities to monitor along with the characteristic of the tax legislation and the level of tax burden on organizations and individuals is an important criterion for assessing the competitiveness of the national tax system.
The purpose of the tax administration is to ensure that tax revenue forecast in the budget system of the country in conditions of optimum combination of methods of tax regulation and control, as well as the most effective mechanism for the functioning of the tax system and tax regulations in terms of the further development of the national economy.
It is important to note that the target settings of tax administration include the fulfillment of tax obligations by the taxpayer; implementation of the tax policy and the challenges faced by the government at this stage; strengthening tax discipline, as well as streamlining of tax relations.
The peculiarity of the tax administration is that it takes the form of a complex system organization of the relationship between taxpayers and tax administration in the face of tax authorities for the execution of the revenue part of the budgets of different levels. Tax administration aims at building a comfortable tax system in a mobile form, in the form of a flexible mechanism that can quickly respond to both external and internal changes. This integrated system is aimed at improving the efficiency of set of rules and regulations governing the tax action, specific technology tax relations and a stable flow of revenues to the budget system.
Tax administration is the most socially expressed sphere of administrative actions. Disadvantages of tax administration lead to a sharp decline in tax revenues, increase the likelihood of tax offenses, they upset the balance of inter-budgetary relations between the regions and the federal center and, ultimately, exacerbate social tensions.
Tax administration is an indicator that allows one to track the effectiveness of existing system of taxes and fees. Moreover, it allows one to optimize the processes of formation of budgetary and extra-budgetary funds, to organize tax relations and create the necessary conditions, including formulating some ideas, suggest bills, etc., necessary for the implementation of financial and regulatory policy.
Tax administration is understood as the realization of the tax administration within its competence the functions and powers established for it by state and by tax legislation. It includes as a major part the tax administration system, i.e., package of measures to: optimize the tax structure, improvement of the mechanism of collection, tax accounting and reporting; control over correctness of calculation, completeness and timeliness of payment of taxes, compliance with established tax laws, rights and obligations of the tax authorities and taxpayers; distribution of tax revenues between the budgets of different levels, the collection and analysis of the results; preparation of proposals to improve their effectiveness; harmonization of tax relations of all participants of the taxation process [2]. similar to M.T.Ospanov's understanding of the nature of tax administration is the oneof V.A.Krasnitskу and A.Peronko.
Tax administration, according to V.A. Krasnitskiy, is atax relationship management system [3], whose principal objective is to develop new forms of tax relations, adequate to the state of the productive forces. In addition to the basic problem, according to V.A.Krasnitsky, tax administration has other problems: tax revenue prediction for the medium term on the basis of forecast calculations of yield growth of the economy; development of new tax concepts; preparation of tax studies of the protectionist policy of foreign economic activity.
Like V.A.Krasnitskiy, I.A.Peronko considers tax administration as a system of governance of all tax relations complex [4].
These I.A.Peronko's methods and tax administration forms include: forecasting of tax revenues; approval of the tax budget; optimization of tax rates and their share distribution; assessment of region's tax potential, etc. Arutyunov [5] under the tax administration understands activities of public authorities responsible for the full and timely provision of revenues to budgets of all tax (duty) levels and penalty fees and fines, as well as their actions in a criminal prosecution in the circumstances, evidence of the facts of tax
More narrowly than the authors mentioned above, G.Ya.Chukhnina determines the nature of tax administration. In the context of the study of tax controlmechanism andsubjects under tax administration, she understands the organization and implementation of effective activities of tax control subjects [6].
Having considered the various views of the authors, we can determine the overall structure of the tax administration, which is represented in Figure.
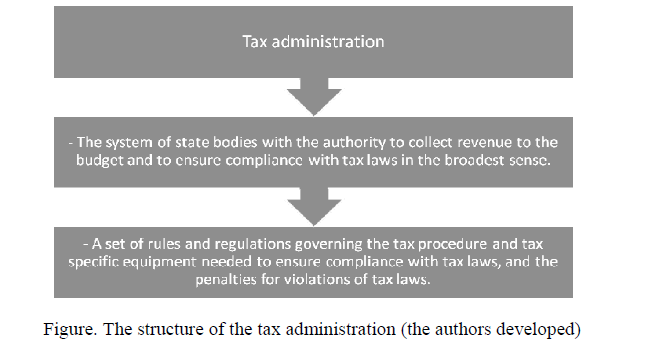
Figure. The structure of the tax administration (the authors developed)
As we can see, the tax administration system is made up of government agencies that have the authority to collect revenue in a budget and a set of rules and regulations governing the tax procedure in the country.
As part of the management process, the administration not only shares the properties with it, but also has special, distinctive features. Administration feature is that, firstly, it is management by the form, i.e. management system of the organization of relations between taxpayers and tax administration in the face of tax authorities in the first place (if it's about tax administration). This is control of observance of external forms of these relations, established by the law and finding its expression in the body of rules and regulations governing the tax action and specific technology of tax relations, sanctions for violation of tax legislation, the powers of the tax authorities. The government receives from the tax authorities a wide information, the analysis of which allows one to draw conclusions about the level of effectiveness of tax policy.
The concept of «tax administration» broadly encompasses many areas of activity and regulation of the state tax system, such as the powers of authorities, rights and obligations of taxpayers and the powers of the tax authorities, tax control procedures, responsibility for tax offenses, complaints procedures and actions of tax authorities and other key concepts used in the tax legislation. In a narrower sense, the term «tax administration» is the organization of the tax authorities and the methods used by its operations. Tax administration should ensure the highest possible collection of taxes, while minimizing the costs, including the administrative burden on taxpayers.
Summarizing views reflected in these scientific papers on the nature of tax administration, apart from the fact that it includes and what are its objectives, we can make two, in our opinion, fundamental conclusions. Firstly, in the above papers, except the one by G.Y.Chukhnina, authors define the essence of the tax administration differently, on the one hand, they almost completely coincide, on the other there's a breadth of interpretation of content of tax administration, which is identified with the concept of «management fees». Moreover, M.T.Ospanov treats the tax administration even wider than the tax administration, which, he said, is only a component of the tax administration. The latter, as a special sphere of activity of the state, in our opinion, authors have associated with the functions of the state government on taxes and duties. It seems that definitions of the tax administration given by them not accurately reflect the essence of the concept, as it is not determined in the process of discursive concepts and empirically. Second, estimations on the tax administration entities are not supported by the theoretical and methodological basis, the corresponding arguments. They are expressed as a paradigm that is a sample that does not require the development of theoretical foundations to express opinions. This reduces the cognitive value estimations, as conceptual and analytical power of the concept remains unclear.
Effective functioning of the tax system in most cases is associated with tax administration methods, which are defined respectively as: tax planning, tax management and tax control, as well as the forms of their realization: tactical and strategic planning, tax incentive system, registration and registration of taxpayers, etc. In this case, tax administration is considered as a system of government tax relationship.
In context of existing variety of conceptual approaches to the identification of nature and content of tax administration, which are the subject of scientific debate, it is possible to introduce the hypothesis about the impact of tax administration in the process of financial and economic activity of subjects of market relations and the parameters of the distribution of gross domestic product, which will form a conceptual model of tax administration on the basis of the evolutionary-systemic approach to the functioning of tax relations and interaction between the participants, in which the tax administration is represented as an element of direct control action, forming a direct connection with the managed objects, and an integral part of the tax system management procedures, as part of tax policy.
Critical analysis of the processes of institutionalization of the tax administration allows one to create a fundamentally new approach to the design of tax administration mechanism, based on implementation of functional-oriented structure of the tax authorities, which determines the efficiency of main methods of tax administration (tax forecasting, tax control, tax control), as well as infrastructure support conditions determining the effectiveness of fiscal activities.
A relatively independent nature of the tax administration is shown in the specific procedures and criteria for evaluating actions (inaction) of relation participants in the sphere of taxes to which the regulatory requirements are laid down in the tax law, which should be considered in theoretical understanding of the nature and the institutional structure of the mechanism tax administration. In view of the above, the effective model of tax administration can be presented as a multi-modal composition of tax administration mechanism, in which there are four main modules: organizing, controlling, functional and institutional and legal. The content of organizational unit provides technical specifications for the implementation of powers of the tax authorities; within the control module fixed are tax control methods and conditions for their implementation; importance of the function module is determined by instruments and procedures of the organization of tax collection, as well as the implementation of tasks, indirectly affecting the observance of fiscal interests of the state (registration and conducting business entities registers, control over cash circulation, licensing and control of operations with excisable goods, representing interests of the state in the affairs of bankruptcy prevention activities); legal construction of the module is represented as a set of laws, normative legal acts of the executive bodies, judicial decisions and local regulatory legal acts providing a formalization of the rules of tax techniques and interaction between the participants of tax relations [7].
In the context of the study of formation and development of the tax administration problem actual is to examine differences between the concept of «management of the tax system» from the tax administration.
Tax management in the broadest sense is the activity of the state to manage the elements of the tax system. At the same time, there are three main elements.
The first element is associated with the collection of taxes and duties and is a legal establishment of the list of tax payments and the procedure for each type of tax and tax collection. The second element is identified with the legal powers of the tax authorities on the organization of work and activities in the tax area (establishment of competence, principles, procedures, forms and methods). The third element is due to the tax authority to determine its function, problems of tax control and bringing to legal responsibility of individuals for violation of tax laws.
Tax management in the narrow sense is the management system of tax authorities. Tax administration is regarded as a "skeletal" tax basis, transforming it into an integrated system. This framework is based on the principle of selection of socio-economic preferences in the formation of concepts, models, state tax system structure, defining the organic unity of its elements. The stability of tax authority system is determined by the tax administration efficiency. Therefore, tax administration is not only a scientific category, but, at the same time, from a practical point isan information system for the regulation of the national economy.
The main elements of tax administration are:
- Monitoring the compliance with tax legislation by taxpayers (by the fee payers);
- Monitoring the implementation and execution of tax legislation by tax authorities;
- Organizational, methodological and analytical support for monitoring activities [8].
There is however, the theory of taxation, a great concept considering the relationship between the management of tax system and tax administration. Thus, under the management system we will understand a hierarchy of links and ties, carrying out management processes in the socio-economic system. The control system used in tax administration, in modern conditions, has a linear direction, i.e., in this case, priority is givento authority and responsibility. In the best case it's just a clear connection, in the worst, many bureaucratic approvals.
Currently, there is an urgent need to completely transform the tax service, turning it into a proactive organization that focuses on high quality control of the execution of the tax legislation and the provision of reference and guidance to law-abiding taxpayers. To do this, the reduction of administrative costs (transaction costs), more efficient use of existing resources of the tax authorities, and most importantly, improving the quality of fiscal control through the use of preventive measures are needed. It is obvious that the main factor of economic success is the quality of the country's laws and policies, on the one hand, and the quality of state institutions on the other. In taxation, the difference between tax system and tax administration (tax authorities) is difficult to find. The «best» tax policy may not «work» if the tax administration is not able to carry it into effect.
Summarizing the study of theoretical and methodological issues related to the essence of the tax administration and the tax authorities in the system of public service delivery functions, we offer the author's interpretation of the concept of «tax administration»:
Tax administration is a management activity of the tax authorities to provide public services to all participants of tax relations in order to improve the efficiency of tax control and tax collection.
In this study, we proposed the following measures to improve the efficiency of tax administration system:
- The creation of a contact center line, a consultative body on the basis of a separate site for each tax administration (region, city, district), linked to the official website of the committee, which will increase the transparency of the tax system, the availability of counseling services for taxpayers, and reduce the level of tax evasion;
- Given the insufficient level of elaboration of the laws governing the calculation of certain taxes, it is necessary to create an electronic database enabling to make payments on certain types of taxes for a wide range of taxpayers (e.g. international studies show that approximately 80% of taxpayers are willing to pay taxes voluntarily, and if they don't, it's because of ignorance of the law, and only 20% of taxpayers evade taxes).;
- To conduct off-site inspections in the system of tax administration on the basis of database segmentation of taxpayers by legal status and size of the business;
- Introduction of balanced scorecard in the activities of tax administrations in terms of reduction of transaction costs for the tax checks and the effectiveness of control measures of the tax authorities over completeness and timeliness of payment of taxes and
References
- Tax The main results of the reform / Zolotareva A., Kireeva A., Kornienko N.; ed. Sinelnikova-Murylyova S.G. and Trunina I. B.; In 3 volumes. Volume 1. Institute of Economy in Transition, Moscow: IET, 2008, 786 p.
- Ospanov T. Tax reform and harmonization of tax relations, Saint Petersburg: Publishing house SPSUEF, 1997, 234 p.
- Krasnitskiy V.A. Tax administration organization (for example, the tax authorities of the Krasnodar Territory), PhD, Thesis: 08.00.10, Krasnodar, 2000, 236
- Peronko I.A. Problems of improving the taxation in the Russian Federation and their solutions, PhD, Thesis, Moscow, 2001, 354
- Arutyunov A.A. Tax administration to ensure timely receipt of tax payments (on the materials of the Federal Tax Service of Russia for Moscow): PhD. Thesis: 08.00.10 Moscow, 2006, 173
- Chukhninа G.Y. The mechanism and the subjects of the tax control in the Russian Federation, PhD, Thesis: 08.00.10, Volgograd
- Ilyasov K.K., Zeynelgabdin A.B., Ermekbaeva B.Zh. Taxes and taxation, Almaty: RIC,
- North D. Institutions, Institutional Change and Economic Performance, trans. from English. A.N.Nesterenko; foreword. and scientific, B.Z.Milnera, Moscow: Fund economic book «Elements», 1997.