In modern conditions increasing effectiveness of teaching foreign language is possible only due to implementation in studying process new teaching methods which allow not only improve students’ level of foreign language but also promote development of such professional qualities as creative way of thinking, which stages of development progress whole life.
The Annual Message of the President of Kazakhstan, N.A.Nazarbayev to the people of Kazakhstan «Socio-economic modernization as the main direction of development of Kazakhstan» noted the relevance of multilingual education, as «one of the most important values; and the main advantage of our country is multiculturalism and multilingualism». In accordance with the objectives set by the President in the State Program for Education Development of the Republic of Kazakhstan for 2011–2020, the State program of functioning and development of languages for 2011–2020. and the cultural program «Trinity of languages» by 2020 all citizens of Kazakhstan should master the Kazakh, 95 % should master Russian and 25 % — English.
At present, according to the State Program of Education Development of Kazakhstan for 2011–2020, there was established a network of specialized schools for gifted children, with learning in three languages. Currently, the republic has 33 schools with three languages teaching. In order to create innovative models of multilingual education in the future, the number of schools offering education in three languages, will increase from 33 to 700.
In modern conditions, increasing the efficiency of foreign language teaching is possible thanks to the introduction in the educational process of new educational methods that will not only allow you to provide students with a high level of language skills, but also contribute to the development of their professional skills such as creative thinking.
It is necessary to consider the existing science division of thought on the productive and reproductive. Z.I.Kalmykova bases this distinction on the «degree of novelty produced in the process of mental activity of the product in relation to the knowledge of the subject» [1].
Productive or creative (creative) thinking — it is a way of thinking that «generates any new knowledge or new material or ideal product (result), for example, new knowledge and new solutions to problems, new scientific discoveries» [2].
Reproductive or non-creative thinking — is thinking, «which opens to the person already known to others the knowledge or recreates what once has already been created by someone». With this thinking, a man, solving problems, follows usually known, previously opened typical way by reproducing previously found solutions, so this kind of thinking does not lead to new results, so this type of thinking became known as uncreative [3–5].
One type of non-creative thinking is convergent thinking. This kind of thinking, according to P.C.Nemov, «is characterized by the same attempts or approaches to the solution of various problems», mechanical transfer of one and the same method of solving problems on other tasks, i.e., «is inflexible, rigid, and only if the used method is not suitable for solving this problem, it remains unresolved. «This kind of thinking» is often found in people with a relatively low level of intellectual development».
In contrast to the convergent thinking, divergent thinking when implemented has «a lot of different approaches to solving the same task or process of moving to the target at the same time in several different directions. His ultimate goal is to find a balanced assessment of all the possible solutions of the problem». This type of thinking, says P.C.Nemov, «often associated with creative thinking, as it meets the definition of a creative (productive) thinking and often does lead to the discovery of new ideas and solutions» [6].
Product creation of divergent or creative thinking is not possible without the use of both logical and critical thinking. For example, in the work on communicative learning situation, which is creative and of solving-problem character, students must critically assess its condition, invent and propose options for its solutions and also critically analyze all variants of its decision and must eventually come to some logical conclusion (design) of the product, for the creation of which the work was carried out.
And even despite the fact that the conditions for the successful use of critical and creative thinking are significantly different, the example of combining the advantages of each of them in the field of practical psychology — in the implementation of such method of controling thinking processes as «brainstorming» in which creative and critical thinking are used equally, but at different stages of the task.
According to the opinion of E.I.Fedotovskaya critical and creative thinking are closely interrelated. In her thesis, the author points out that «we are creative whenever express our thoughts orally or in writing. In this creative thinking is connected with critical». «Critical thinking, the source of which is the conflict or problem, in turn, allows the connection of thinking and feeling, because the solution of any problem is related to the choice of values, feelings and expression of a demonstration of his own inclinations». Therefore, the «emotion, imagination, values are the building blocks of critical thinking», So, we can follow D.Halpern [6] and say that critical thinking, in fact, is one of the creative thinking.
The teaching process at schools focuses mainly on the development of the form of thinking, developing skills of analysis, i.e. — teaching students how to understand the requirements, follow or create a logical argument, figure out the answer, eliminate the incorrect paths and focus on the right. Critical and creative ways of thinking are important for the successful study and work, but the latter is not very well developed, studied, and so in most cases ignored in higher education. The main distinguishing features of these two types of thinking have been proposed by Robert Haris [2]. Data are presented in table1:
T a b l e 1
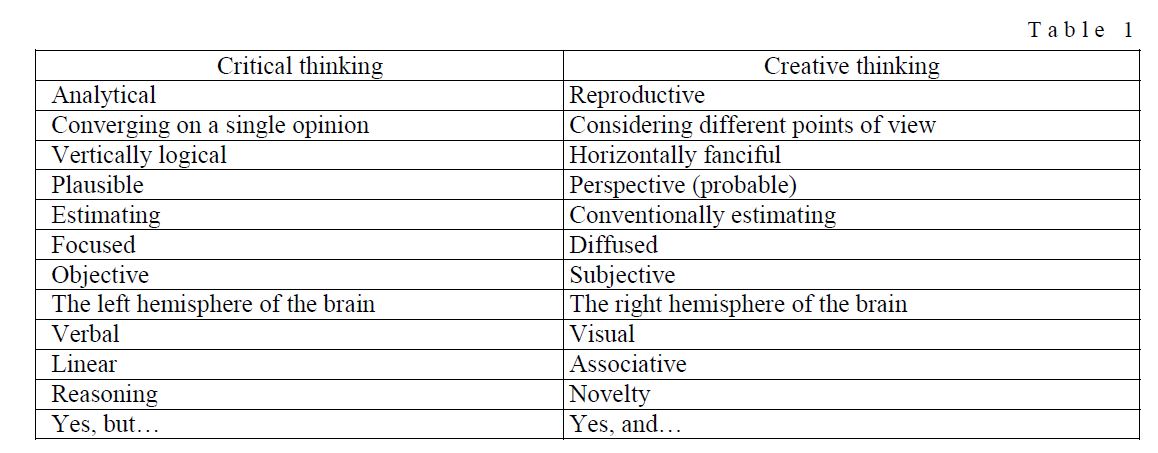
In any activity to deal with any mental problems, the two types of thinking are very important. First of all, any problem should be analyzed and for this there is a generation of possible solutions; Next, you must select and implement the best solution, and finally, it is necessary to evaluate the effectiveness of the solution. This process shows the alternation between these two kinds of thinking, critical and creative. In practice, both types of thinking work together and are not really independent from one another.
Purposeful perfection of creative thinking skills of each person is possible and necessary, because creativity leads to development.
Therefore the factors that are necessary for the development of creative abilities, are very interesting for us. In the book «How pissible creative thinking is?» I.A.Beskova points out that it is important to:
- «accumulation of knowledge, intellectual and cognitive abilities, broadening of the worldview;
- acquisition of diverse experience;
- ability to form individual opinions, beliefs, and even the illusion based on experience» [7].
The meaning of R.Sternberg is also interesting, who believes that the creative manifestation of personality is determined by six main factors:
- intelligence as the ability (The author believes that the intelligence and creativity form a single factor);
- knowledge;
- style of thinking;
- individual characteristics;
- motivation;
- surroundings [8].
R.Sternberg as well as de Bono believes that creativity requires independent thinking stereotypes and external influences, as well as the necessary creative environment, without which it is impossible to work.
Creative environment is the creation of favorable psychological conditions, certain favorable psychological climate for the creation, formation and implementation of the existing students' creativity, stimulating and motivating individual work.
In determining the educational goals and objectives of improving learning English speech by developing creative (creative) thinking it is necessary to clearly understand to what the components of creative thinking is necessary pay attention to develop them. As creative (creative thinking), according to E.I.Fedotov, suggests the following skills, we also proceeded from the need to take them into account. These skills are as follows:
- «mental experimentation, spatial imagination;
- independent transfer of knowledge to solve new problems, challenges, new solutions;
- ability of a combination of previously known methods, ways of solving the problem, the problem in the new (complex) way;
- ability to more efficiently handle conflicting
- ability to resist the inclination to make the usual judgment familiar things;
- ability to resist stereotypes, patterns of thinking and do not be afraid to reject all that comes with them in any obvious contradiction» [9].
Defining creative thinking we can distinguish this term as:
- An Ability. A simple definition is that creativity is the ability to imagine or invent something new. As we will see below, creativity is not the ability to create out of nothing (only God can do that), but the ability to generate new ideas by combining, changing, or reapplying existing ideas. Some creative ideas are astonishing and brilliant, while others are just simple, good, practical ideas that no one seems to have thought of
- Believe it or not, everyone has substantial creative Just look at how creative children are. In adults, creativity has too often been suppressed through education, but it is still there and can be reawakened. Often all that's needed to be creative is to make a commitment to creativity and to take the time for it.
- An Creativity is also an attitude: the ability to accept change and newness, a willingness to play with ideas and possibilities, a flexibility of outlook, the habit of enjoying the good, while looking for ways to improve it. We are socialized into accepting only a small number of permitted or normal things, like chocolate-covered strawberries, for example. The creative person realizes that there are other possibilities, like peanut butter and banana sandwiches, or chocolate-covered prunes.
- A Creative people work hard and continually to improve ideas and solutions, by making gradual alterations and refinements to their works. Contrary to the mythology surrounding creativity, very, very few works of creative excellence are produced with a single stroke of brilliance or in a frenzy of rapid activity. Much closer to the real truth are the stories of companies who had to take the invention away from the inventor in order to market it because the inventor would have kept on tweaking it and fiddling with it, always trying to make it a little better.
The creative person knows that there is always room for improvement.
In the context of creativity one of the most important issues of educational psychology at the moment is the question of creative and cognitive abilities, without which the creative process is impossible. That is why the question about abilities is interesting. According to B.M.Teplov, the concept of "capacity" consists of three main ideas:
- «under the abilities are understood individual psychological characteristics that distinguish one person from another»;
- «abilities are not all the individual features, but only those that are relevant to the successful execution of any activity or many activities»;
- «the concept of ability «is not limited to the knowledge, skills or abilities that are already developed this person» [10].
The process of formation of creative thinking in humans occurs throughout their whole life, from early childhood. During their studies in secondary schools of general education students form creative thinking, that means addressing issues related to the general education disciplines. Given the innovations in the field of education and having open access to the world teaching experience, understanding that «every child is talented in his own way», defines the objectives, content and form of the organization of schooling. The use of modern pedagogical, technical and information technology in the educational process, creates the conditions for disclosure of abilities and realize the potential of each child, taking into account the interests and abilities of each child. The data are presented in Sheme 1 at each educational degree: at the elementary, middle and high school it has its own priorities. For younger students it is to learn, to read and write, to give basic knowledge of the basic sciences: mathematics, social studies and science; instill confidence through dance, music, in the studio theater.
At secondary school, the child is attached to the research activities in various fields of natural sciences and humanities, understands the basics of programming and acquires basic economic-analytical competence.
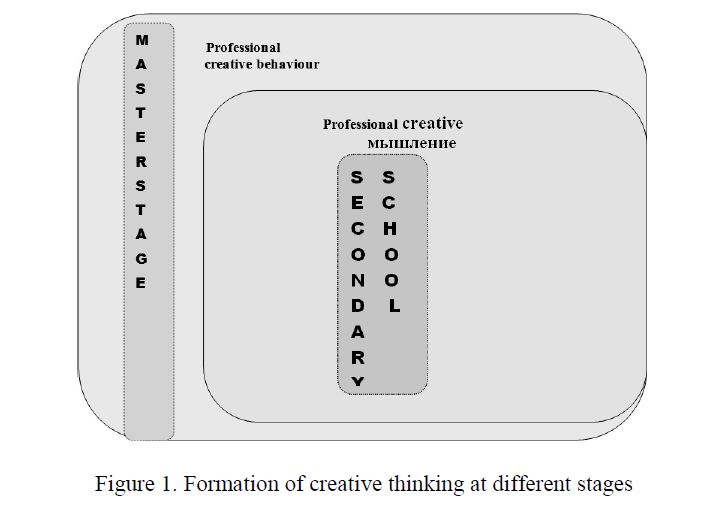
Figure 1. Formation of creative thinking at different stages
At high school, when the student has already decided on the choice of future profession, he has the opportunity to study profile subjects in depth, parallel with participating in interdisciplinary projects, integrated lessons that is now relevant in the educational institutions of Kazakhstan.
During their studies for a bachelor degree professional creative thinking with the fundamentals of professional creative behavior is formed, and as part of master degree, professional creative behavior is formed.
At the postgraduate stage professional creative behavior is laid, whose foundations are based in the framework provided by SCSO of KR in pedagogical and professional practices.
The most perfect form of professional work in modern conditions is transformative, innovative, creative and creative activity of a professional. Before you begin to consider the formation of creative behavior and thinking within the postgraduate education should be considered graduates of undergraduate, competence formed the training and provides the basis for a master degree. Graduates of the Bachelor's degree in any specialty must be prepared to undertake such development activities. Formation of the basic competences of a bachelor must take place in the framework of formation of creative thinking, as the credit technology itself involves independent learning activities of the student and thus prepares him for the creative development of professional conduct, which is one of the main priorities of post-graduate education.
On the basis of qualifications of «Qualification handbook for managers, professionals and other employees» approved by order of the Minister of Education and Science of the Republic of Kazakhstan from 12.02.2008 № 61, a bachelor may in the prescribed manner carry out professional activities in accordance with the received basic and specialized training in foreign language specialty.
Thus, a graduate of Bachelor's degree already owning the above competencies, having the basics of professional creative thinking, which is formed not only within the training sessions, but also educational and professional practices, enters the Masters degree studying where he continues to improve as a competent, critical and creative thinking expert in the field of foreign languages [11].
The creative person has a wide range of specialist qualities. Among the most important qualities of the creative person we can divide three groups:
- qualities, characterizing the overall activity of the person (activity, energy, perseverance, initiative, determination, commitment, enthusiasm, independence, power, perseverance, enthusiasm, optimism, confidence, sustained interest, and );
- qualities, characterizing attitudes toward activities (responsibility, discipline, hard work, diligence, seriousness, objectivity, diligence, organization, productivity, observation, creative approach, and others);
- intellectual qualities (broad-mindedness, critical thinking, logical thinking, depth of thought, liberty of thought, intelligence or level of development, erudition, insight, learning, and others).
That is why in the educational process are the formation of creative thinking, the development of creative abilities consistent with the objectives of a modern specialist training are in priority. Creative professional behavior is seen as a set of capabilities to realize the potential creativity of the future specialist in the educational process of the university on the basis of the development of creative thinking, intelligence, and professional invariant through the mechanisms of self-actualization, learning Innovation, forming the indirect effects and the main result — a creative professional behavior. Conditions for the development of creative professional conduct are the person's ability to engage in constructive, unconventional thinking and behavior, as well as reflection, i.e., the awareness and the development of his own experience; professional advance training, focused on the potential multi-variant uncertainty and incomplete, the presence of images of creative behavior and others.
Thus, we can say that creativity in all its forms and manifestations at different levels of education is relevant activity and such thinking justifies social needs of society. For the formation of creative thinking of students specialists with creative behavior are needed. Thus, the more we form a creative teacher behavior, the greater the potential for the formation of creative thinking of students it has. This process is a spiral movement, where each turn is becoming more sophisticated.
Management of processes of formation and development of the creative potential in learning provides professional development and the development of the creative personality, namely, self-actualization and self-expression in the work of the student, the training of creative thinking and acting professional, the formation of a creative oriented person, creation of a fully and harmoniously developed personality.
References
- Psychological Dictionary / Edit. by V.P.Zinchenko, B.G.Meshсherуakova, Moscow: Ped-Press, 1997, 440
- Yenikeyev M.I. Fundamentals of general and legal psychology, Moscow, 1996, 126
- Torrance Ye.P. Education and creative potential, Minneapolis,
- The concept of foreign language education RK, Almaty: Kazakh University of International Relations & World Languages, 2006.
- Rubinshteiyn S.LI. Fundamentals of General Psychology, Saint Petersburg: Izdatel'stvo «Piter», 2000, 712
- Nemov R.S. Psychological Dictionary / R.S.Nemov, Moscow: Gumanitar, izd. centr VLADOS, 2007, 560 e.: il., 224
- Kalmykova Z.I. Productive thinking as a basis for learning, Moscow: Pedagogika, 1981, 200
- Halpern D. Psychology of critical thinking, Saint Petersburg: Izd. «Piter», 2000, 512
- Fedotovskaya Ye.I. The technique of critical thinking as an important factor in the formation of foreign language communicative competence in specialized high schools (for example, socio-political subjects, English): ... cand. of ped. sciences / RAO Institute of content and teaching methods, Moscow, 2005, 194 p.
- Storozhenko A.M. Topical issues of social consciousness and culture in the conditions of mature socialism, Kuiybyshev, 1981, p. 226–244.
- Fel'dshteiyn D.I. Developing personality psychology, Moscow-Voronezh: Izd. MPSI,